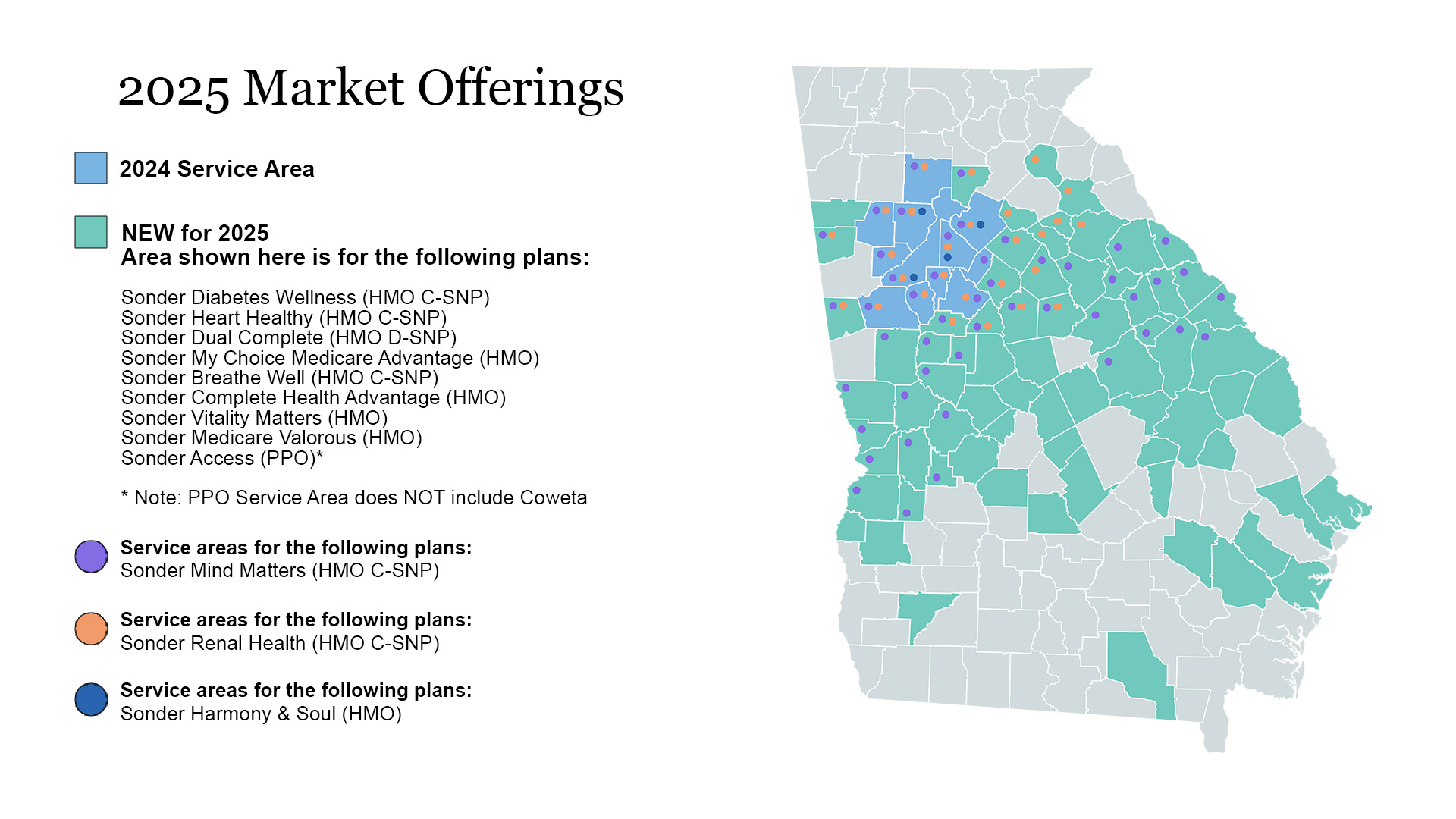
When it comes to Medicare options, Georgia residents have two primary choices: Original Medicare and Medicare Advantage. Each offers unique benefits and considerations. This blog post will help you understand these options, so you can have an informed conversation with an insurance representative about which plan best meets your needs.
What is Original Medicare?
Original Medicare is the traditional fee-for-service program offered directly by the federal government. It consists of two parts:
Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance)
Covers inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility care, hospice, and some home health care.
Most people don’t pay a premium for Part A if they or their spouse paid Medicare taxes while working.
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance)
Covers doctor visits, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services.
Part B has a monthly premium, which is typically deducted from your Social Security benefits.
Key Features of Original Medicare:
- Flexibility: You can visit any doctor or hospital that accepts Medicare, anywhere in the U.S.
- Standardized Coverage: The benefits are the same regardless of where you live, although costs can vary.
- No Network Restrictions: There are no networks, so you are not limited to specific providers or facilities.
What is Medicare Advantage?
Medicare Advantage (MA), also known as Medicare Part C, is an alternative to Original Medicare offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare. These plans provide all the benefits of Part A and Part B, and often include additional benefits.
Types of Medicare Advantage Plans:
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): Leverages a network of doctors and hospitals, often needing a referral to see a specialist.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): Offers more flexibility by allowing you to see any doctor, but you pay less if you use network providers.
Special Needs Plans (SNP): Tailored for individuals with specific diseases or characteristics.
Private Fee-for-Service (PFFS): You can see any Medicare-approved doctor if they agree to the plan’s payment terms.
Key Features of Medicare Advantage:
Additional Benefits: Many plans offer benefits not covered by Original Medicare, such as dental, vision, hearing, and wellness programs.
Out-of-Pocket Maximum: Provides a cap on how much you spend on covered services annually, which Original Medicare doesn’t offer.
Bundled Services: Most include Part D (outpatient prescription drug coverage), which is purchased separately with Original Medicare.
Network Restrictions: Plans often have networks of doctors and hospitals you must use to get the lowest costs.
Comparing Costs
Original Medicare:
Premiums: Most people pay no premium for Part A, but there is a standard premium for Part B.
Deductibles and Coinsurance: Part A has a deductible for each benefit period. Part B has an annual deductible and typically covers 80% of the cost of services, leaving you with 20% coinsurance.
No Out-of-Pocket Maximum: You could pay a significant amount if you need a lot of healthcare services.
Medicare Advantage:
Premiums: You still pay the Part B premium, and some MA plans have an additional monthly premium.
Cost-Sharing: May have lower out-of-pocket costs for some services, but costs can vary widely between plans.
Out-of-Pocket Maximum: Limits how much you will pay in a year for covered services, providing financial protection.
Prescription Drug Coverage
Original Medicare:
Part D: You need to purchase a standalone Part D plan for outpatient prescription drug coverage. These plans vary in cost and coverage.
Medicare Advantage:
Integrated Part D: Many MA plans include prescription drug coverage, simplifying your coverage and potentially saving you money.
Enrollment and Eligibility
Original Medicare:
Eligibility: Generally available to people 65 and older, and to some younger people with disabilities or specific conditions like End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD).
Enrollment Periods: Initial Enrollment Period (IEP), General Enrollment Period (GEP), and Special Enrollment Periods (SEPs) based on qualifying life events.
Medicare Advantage:
Eligibility: You must be enrolled in both Part A and Part B to join an MA plan.
Enrollment Periods: Initial Coverage Election Period (ICEP), Annual Election Period (AEP), and Special Enrollment Periods (SEPs).
Making Your Decision
Choosing between Original Medicare and Medicare Advantage depends on your individual needs and preferences.
Consider Original Medicare if:
You value flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
You frequently travel within the U.S. and want coverage wherever you go.
You don’t mind managing separate plans for medical and prescription drug coverage.
Consider Medicare Advantage if:
You want additional benefits beyond what Original Medicare offers.
You prefer the convenience of having all your healthcare services bundled into one plan.
You are comfortable using a network of providers and managing plan-specific rules.
Conclusion
Understanding your Medicare options is crucial to making an informed decision. Whether you choose Original Medicare or a Medicare Advantage plan, ensure that your choice aligns with your healthcare needs, budget, and lifestyle. For Georgians turning 65 or those looking to change their coverage, reviewing these options thoroughly will help you select the best plan for your situation.
For more personalized advice, consider speaking with a licensed Medicare advisor who can help you navigate your options and find the plan that’s right for you.